Author(s)
Mohamed S. El Naschie
The supposedly missing dark energy of the cosmos is found quantitatively in a direct analysis without involving ordinary energy. The analysis relies on five dimensional Kaluza-Klein spacetime and a Lagrangian constrained by an auxiliary condition. Employing the Lagrangian multiplier method, it is found that this multiplier is equal to the dark energy of the cosmos and is given by 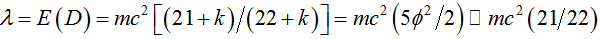 where E is energy, m is mass, c is the speed of light,
where E is energy, m is mass, c is the speed of light, 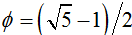 and λ is the Lagrangian multiplier. The result is in full agreement with cosmic measurements which were awarded the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics as well as with the interpretation that dark energy is the energy of the quantum wave while ordinary energy is the energy of the quantum particle. Consequently dark energy could not be found directly using our current measurement methods because measurement leads to wave collapse leaving only the quantum particle and its ordinary energy intact.
and λ is the Lagrangian multiplier. The result is in full agreement with cosmic measurements which were awarded the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics as well as with the interpretation that dark energy is the energy of the quantum wave while ordinary energy is the energy of the quantum particle. Consequently dark energy could not be found directly using our current measurement methods because measurement leads to wave collapse leaving only the quantum particle and its ordinary energy intact.

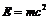 when multiplied by a scaling parameter
when multiplied by a scaling parameter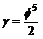 where
where  is Hardy’s quantum entanglement and
is Hardy’s quantum entanglement and 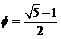 . Furthermore
. Furthermore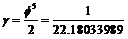 could be approximated to
could be approximated to 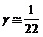 and thus may be interpreted as the inverse of the compactified bosonic strings dimension
and thus may be interpreted as the inverse of the compactified bosonic strings dimension 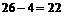 .
.